Journal of Agriculture and Crops
Online ISSN: 2412-6381
Print ISSN: 2413-886X
Print ISSN: 2413-886X
Quarterly Published (4 Issues Per Year)

Archives
Volume 9 Number 3 July 2023
Effect of Drying on the Blends of Tomato-Pepper-Turmeric Powder
Authors: Musa Omotayo Jimoh ; Emmanuel Adediran Alamu ; Oluwafemi Seun Adeoye
Pages: 413-420
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.413.420
Abstract
Tomatoes and pepper are inevitable ingredients in food preparation and the need to minimize their losses cannot be over-emphasized. Matured red tomato, pepper and turmeric sourced locally were cleaned, sliced (10-15 mm) and dried using vacuum oven (60 oC for 14 h). Fresh blends of tomato, pepper and turmeric (RBA and RBB) and dried blends of tomato, pepper and turmeric (DBA and DBB) samples were analyzed for proximate, selected minerals, vitamin, phytochemical and sensory properties. Moisture, ash, protein, fat, fiber and carbohydrate content in DBA was 18.26 %, 11.95 %, 14.31 %, 3.77 %, 3.08 % and 48.89 %; and 16.80 %, 14.78 %, 13.04 %, 4.28 %, 3.21 % and 51.41 % in DBB. Calcium and iron content in DBA was 102.63 mg/100g and 78.90 mg/100g; while in DBB, 114.25 mg/100g and 81.35 mg/100g respectively. However, dried samples had no significant difference in magnesium, potassium, sodium and zinc content (p ˃ 0.05). Ascorbic acid and β-carotene in DBA and DBB was 73.90 mg/100g and 66.48 mg/100g; and 71.28 mg/100g and 59.27 mg/100g respectively. Carotenoids, phenol and flavonoids in DBA and DBB were 510.38 mg/100g, 425.60 mg/100g and 1040.88 mg/100g; and 512.86 mg/100g, 429.10 mg/100g and 1035.26 mg/100g respectively. Inclusion of turmeric improves phytochemical properties of the blends and enhances consumer acceptability.
How to Cite: Musa Omotayo Jimoh, Emmanuel Adediran Alamu, Oluwafemi Seun Adeoye, 2023. "Effect of Drying on the Blends of Tomato-Pepper-Turmeric Powder." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 413-420.
Timing of Floral Differentiation in Four Avocado (Persea Americana Mill.) Cultivars on the Main Island of Okinawa Prefecture, Japan
Authors: Takaaki Maeda ; Yoshimi Yonemoto ; Md. Amzad Hossain
Pages: 408-412
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.408.412
Abstract
We conducted a morphological investigation of flower bud differentiation in four cultivars of avocado (Persea americana Mill.): ‘Pinkerton’ (Guatemalan hybrid), ‘Simmons’ (West Indian), ‘Hass’ (predominantly Guatemalan × Mexican), and ‘Monroe’ (Guatemalan × West Indian). The avocado cultivars were planted on the main island of Okinawa Prefecture, which is the only subtropical area of Japan. Buds were collected on 15 November, and 1 and 19 December, 2011, and on 4 and 17 January 2012. The buds were sectioned longitudinally at a thickness of 15 μm through paraffin sectioning, double-stained with Safranin O and Fast green, and observed under an optical microscope to morphologically determine the flower bud differentiation stage. Flower bud differentiation occurred earliest in ‘Pinkerton’ in mid-December, followed by ‘Simmons’ in early January and ‘Hass’ in mid-January. Flower bud differentiation was not observed in ‘Monroe’ during the study period.
How to Cite: Takaaki Maeda, Yoshimi Yonemoto, Md. Amzad Hossain, 2023. "Timing of Floral Differentiation in Four Avocado (Persea Americana Mill.) Cultivars on the Main Island of Okinawa Prefecture, Japan." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 408-412.
Characterization of Native and Modified Fermented Smoked Cassava for Food Packaging Application
Authors: Adewumi Funmilayo Deborah
Pages: 400-407
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.400.407
Abstract
The goal of this study is to see what changes may be made to fermented smoked cassava (FSC) for use in food packaging. For 5 days, cassava was soaked in water. The fermented cassava was shaped into balls and dried at 50oC d in an oven. The fermented smoked cassava that resulted was milled. The fermented smoked cassava was subjected to chemical modification by pregelatinized phthalation. To make pregelatinized phthalated, FSC, the FSC was pre-gelatinized by heating the solution above 70°C and esterified with phthalic anhydride. The characteristics of modified and native FSC were investigated. The native FSC typical spherical form had vanished, and a fibrous-like irregular structure had replaced it, according to the results of scanning electron microscopy. After some alterations The degree of crystallinity in the native FSC has changed to amorphosity in the modified FSC, according to X-Ray Diffractometry. Thermogravimetry findings demonstrated that the native structural matrix of FSC was totally collapsed at 380oC, whereas the modified FSC structural matrix fully collapsed, leaving just residues at 700 oC. The modified fermented, smoked-dried cassava was discovered to be a promising alternative biopolymer for food packaging applications.
Brief Review: Climate Change and Its Impact on Mango Pests and Diseases
Authors: Lee Yit Leng ; Osumanu Haruna Ahmed ; Mohamadu Boyie Jalloh, et. al.
Pages: 391-399
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.391.399
Abstract
Climate change is negatively impacting the agricultural sector. This review focuses on the effects of climate change on mango pests and diseases, the unknown aspects of this problem, and possible mitigation measures. In addition, mango is susceptible to several pests and diseases infestation at all its stage of life. The major abiotic factors associated with climate change that affect mango pests and diseases include changes in precipitation, wind variability, increased temperature, increases in atmospheric CO2, and changes in light intensity. These factors affect mango pests and diseases in various dimensions in one way or another, including increased activity, growth, development, reproduction, distribution, and migration. These abiotic factors also influence plant growth, development, and reproduction. These interacting factors are complex, and further studies are needed to obtain relevant data to understand the relationships between these factors and pests occurrence. Developing predictive models from these data and intercropping with aromatic plants will be useful for strategies to mitigate the devastating effects of pests and diseases occurrence on mango crops and food security.
Effect of Aloe-Coating Application on Quail Egg Quality During Storage
Authors: Ni Ketut Mardewi ; Luh Suriati ; Ni Made Defy Janurianti
Pages: 384-390
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.384.390
Abstract
Consumption of quail eggs is currently increasing. Quail eggs not only taste good but also contain protein, fat, carbohydrates, and ash. Despite having a shell as a natural protector, quail eggs are very fragile. The surface of the eggshell has small pores that allow the mass transfer. Permeation causes changes in viscosity, weight loss, and albumin liquefaction during storage. Coating application can maintain the internal freshness of eggs by closing the pores to reduce mass transfer and be an anti-microbial. Coating of aloe vera gel (Aloe-coating) is very potential because it contains polysaccharides and bioactive compounds glucomannan and acemannan. The purpose of this study was to determine the concentration of Aloe-coating to maintain egg viscosity and pH and to determine its effect on the quality of quail eggs during storage. The research design used a completely randomized design with a factorial pattern with three repetitions. The concentration of Aloe-coating is the first factor (100%, 75%, 50%, 25%). The second factor is storage time (1, 2, 3, 4 weeks). The observed variables were water content, weight loss, acidity, viscosity, yellow color, egg white height, and Haugh Unit. The research data were analyzed quantitatively using the analysis of variants. The results showed that Aloe-coating had a very significant effect on water content, weight loss, pH, viscosity, yolk color, and quail egg haugh unit. The best concentration of Aloe-coating to maintain the quality of quail eggs is 100%. The use of Aloe-coating can maintain the quality and extend the shelf life of quail eggs.
Indole-3-acetic Acid (IAA) Assisted Phyto-extraction Potential of Ipomoea aquatica Exposed to Lead (Pb) Stress
Authors: Prosenjit Sarker ; Shahin Imran ; Newton Chandra Paul, et. al.
Pages: 376-383
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.376.383
Abstract
Agricultural lands are gradually being contaminated by heavy metals (HMs) obtained from urbanization and human activities. Lead (Pb) is one of the major heavy metals easily enters into food cycle and causes different health abnormalities. So elimination of this dangerous heavy metal from surface water is crucial and in this regard phyto-extraction based phytoremediation is an environmentally safe procedure. Again, this removal process can be amplified through the use of plant growth regulators exogenously. With this aim, an experiment was conducted to know the efficiency of the use of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) on phyto-extraction of Pb by an aquatic hyper-accumulator plant Ipomoea aquatica. The plants were grown hydroponically with 200ppm Pb treated with 200ppm IAA exogenous spray or mixed with Hoagland solution (HS) or both. The control treatment was HS supplemented with Pb. From the experiment, it was observed that control treatment causes a great reduction in growth parameters as the plants suffered from Pb stress. Treatment with Control + IAA (spray+dissolve), produced tallest plants, longest roots and maximum dry weight. On the other hand, these parameters were got declined in case of Pb treated plants (control). Maximum Pb were accumulated on root, stem followed by leaf for Control + IAA (spray+dissolve). Control treatment caused less Pb accumulation on plant parts. So, maximum bioaccumulation factor (BCF) in root, shoot and leaf were 35.87, 15.33 and 9.15 respectively for Control + IAA (spray+dissolve) treatment. In case of root to shoot translocation, the maximum translocation factor (TF) value (0.5118) was found for Control + IAA (spray) than other treatments. Again for shoot to leaf, the maximum TF value (0.6051) was for HS + HM treatment (Control) and minimum TF value (0.4469) was observed for Control + IAA (spray). From the study, it is confirmed that, exogenous indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) successfully assist Pb phyto-extraction from aquatic bodies and Ipomoea aquatica is a potential heavy metal hyper-accumulating plant.
In Vitro Antagonistic Action by Bacillus Velezensis Strain LP16S Against Cotton Wilt Pathogens
Authors: Louis K. Prom ; Enrique G. Medrano ; Jinggao Liu
Pages: 372-375
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.372.375
Abstract
Cotton productivity and profitability are hampered by several biotic stresses, including the two most destructive wilt pathogens Verticillium dahliae and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum (FOV). In this study, an in vitro assay was conducted to determine the activity of Bacillus velezensis LP16S against three V. dahliae isolates and six F. oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum isolates. Among the fungal isolates, the response when exposed to the B. velezensis LP16S strain in a half-strength potato dextrose agar plate varied markedly. Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum isolates FOV11, FOV 944, and FOV Tx8 were tolerant, while FOV Tx39, FOV 1073, and the three V. dahliae isolates were highly sensitive to B. velezensis LP16S. In conclusion, this Bacillus sp. strain has potential for use in managing these damaging cotton diseases.
Development Strategy and Existing Qualities of Honeybee in Beekeepers Group Badung Regency-Bali
Authors: I Gede Pasek Mangku ; I Gusti Bagus Udayana ; Hanilyn Aguilar Hidalgo, et. al.
Pages: 365-371
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.365.371
Abstract
The cultivation of local honeybees is one of the new alternative jobs for the local community in Badung Regency, Bali to survive their life during Covid-19. This research aims to identify and determine of development strategy and to evaluate the quality existing of honeybees. The total sample was used 50 respondents consisting of 22 members of beekeepers of the “Sarining Trigona Pertiwi” group, 4 samples from local government, 4 from related institution government, and 20 local people. The SWOT method is used to formulate appropriate strategies and IE matrix is to analyze the condition of the honeybee-tourism strategy. The results of the analysis showed that internal factors have a total value of 3.20, with the highest factor being strategic partners in product innovation development. External factor analysis has a total value of 2.88 with the highest factor being increasingly diverse product diversification. Based on the IE matrix, tourism in quadrant IV shows the potential development of honeybees in Badung Regency, Bali is in a position to grow and develop with the appropriate intensive and integrated strategy. Based on the SWOT matrix were obtained strategies to conduct socialization of the cultivation program, having a research program regularly, developing products based on consumer demand, collaborating with cooperatives and Banks in credit services, conducting marketing and good market expansion, making SOP in the process, manufacture and storage of products, government policies on reforestation and forest area protection, human resource training, preparing market analysis and strategies, alternative food sources for the honeybees, and increasing product development. However, the qualities of Tetragonula laevicep honeybees produced by the beekeeper of “Sarining Trigona Pertiwi” are still lower than Indonesia National Standard (SNI) therefore; need to increase the quality in the future.
Characteristics of Aloe-buni Powdered Drinks with the Addition of Arabic Gum and Drying Temperature Variations
Authors: Luh Suriati ; I Gede Pasek Mangku ; Hanilyn Hidalgo, et. al.
Pages: 357-364
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.357.364
Abstract
Aloe-buni is a functional drink of Aloe vera gel and buni fruit extract, containing fiber and antioxidants that are beneficial to health. Processing of Aloe-buni powder drinks using the foam mat drying method requires arabic gum filler to form powder. The drying temperature also greatly affects the manufacture of powdered drinks. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of gum arabic concentration and drying temperature on the characteristics of Aloe-buni powdered drink. This study used a two-factor factorial plan, namely the concentration of arabic gum filler material 10%, 20%, 30% and drying temperature consisting of 30°C, 40°C and 50°C. The results showed that the concentration of gum arabic and the drying temperature were different from the characteristics of the Aloe-buni powdered drink. The best characteristics of Aloe-buni powdered drink were obtained of a concentration 30% arabic gum and a heating temperature of 40°C, as for a pH value of 4.30; total dissolve solid 41.33°Brix; color a* 4.86; moisture content 5.61%; solubility 98.56%; antioxidant activity 7.46%; and vitamin C 66.06 mg/100g.
Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Evaluation of Various Parts of Gossypium Herbacium (Linn) Plant
Authors: Idowu Olajumoke Tolulope
Pages: 353-356
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.353.356
Abstract
The methanol extracts of the various plant parts were screened for anti-oxidant activity by thin layer chromatography using 2,2-diphenyl-1-dipicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) while in vitro antimicrobial evaluation was determined by agar diffusion method and bioautographic technique using Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as test organisms; aqueous solvent served as control and ciprofloxacin served as standard drug. The result showed that methanol extracts of the stem, leaf, root and seed of the plant were found to be stronger against the entire test organisms and the stem and leaf of the plant were also found to possess strong antioxidant activity. The antimicrobial property shown by the leaf is an evidence of the ethno medicinal uses of the plant. G. herbaceum leaf, seed, epicarp, stem bark, root bark, may provide novel plant-derived therapeutic agents, effective in treating infectious diseases arising from multiple drug-resistant bacteria and a target in the management of oxidative stress that could easily lead to aging.
Influence of Novel Freezing and Storage Technology on Nutrient Contents, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of Black Eggplant
Authors: Yousif A. Elhassaneen ; Ghada M. ElBassouny ; Omar A. Emam ; Sherouk H. Hashem
Pages: 338-352
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.338.352
Abstract
The present work aims to study some technological aspects related to the preservation of black eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) fruits by freezing process. Also, the influence of such preservation method on the chemical composition, nutritional value, bioactive compounds content and antioxidant capacity of eggplant fruits will also determine. In fresh eggplant fruits, water is by far the most abundant components with 90.21% of the total fruit weight and fiber is particularly abundant (2.98%). Also, fruits has s moderate levels of vitamins (A, B3, B9, C, E and K) and minerals (P, Mg, Ca, Na, Fe, and Zn) but are relatively rich in K. Phenolics was reported the most abundant bioactive compounds, followed by anthocyanins, flavonoids and β-carotene. The high content of bioactive compounds in the eggplant samples was met with a high level of antioxidant capacities, which was determined by several different methods. The freezing method (slow freezing with grilling pretreatment) that was applied in this study led to cause slightly loses of all studied vitamins by the ratio of ranged -0.88 to -10.97%, and significant (p≤ 0.05) losses of bioactive compounds ratio of ranged -2.52 and -10.23% as compared with the fresh samples, respectively. In contrary, freezing has been shown to cause significant (p≤ 0.05) increase of antioxidant capacities by 4.57 and 11.74% for antioxidant activity and trolox equivalent (TE) assays, as compared with the fresh samples, respectively. Also, prolonging the storage period for six months at -180C did not have a significant effect on all previous measurements. In conclusion, the use of this new and effective method in eggplant preservation may contribute to increasing the economic importance of this product by making it available in the markets regularly throughout the year, easing of export, and increasing the income of the producing countries.
How to Cite: Yousif A. Elhassaneen, Ghada M. ElBassouny, Omar A. Emam, Sherouk H. Hashem, 2023. "Influence of Novel Freezing and Storage Technology on Nutrient Contents, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of Black Eggplant." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 338-352.
Evaluation of Maize (Zea mays) Genotypes forTolerance to Drought using Yield Based Tolerance Indices
Authors: Md. Abdul Mannan ; Ferdousi Begum ; Md. Abdullah Al Mamun ; Md. Ahsan Habib
Pages: 329-337
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.329.337
Abstract
A pot trial was conducted at the Department of Agronomy, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman University of Agriculture, Gazipur from November 2021 to March 2022 to identify relatively tolerant maize genotypes based on growth, yield, yield stability and stress tolerance. indexes. Twenty maize genotypes, including CML-580, CML-563, CML-591, CML-579, CML-588, CML-593, CML-564, BD-814, BD-821, BD-824, BD-10242, BD-811, BD-826, BD-837, BD-808, BD-10237, and BD-10240, were grown under control conditions (80% of field capacity, FC) and drought conditions (40% of FC) following completely randomized design with three replications. Plant and cob height, days to maturity, cob length, cob girth, number of rows/cob, and kernel yield/plant were recorded. Drought stress reduced plant height, cob height, cob length, cob girth, number of rows/cob, and finally maize yield, but increased the days to maturity. Among the maize genotypes, CML-593, CML-564, BD-814, and BD-821 had the lowest decrease in kernel yield, while BD-808 and BD-813 had the highest decrease. Genotypes CML-593, CML-564, BD-814, and BD-821, on the other hand, demonstrated a higher yield stability index and stress tolerance index. Based on their yield and stress tolerance index, genotypes CML-593, CML-564, BD-814, and BD-821 appear to be drought tolerant, whereas BD-808 and BD-813 appear to be drought sensitive.
How to Cite: Md. Abdul Mannan, Ferdousi Begum, Md. Abdullah Al Mamun, Md. Ahsan Habib, 2023. "Evaluation of Maize (Zea mays) Genotypes forTolerance to Drought using Yield Based Tolerance Indices." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 329-337.
Operational Issues of Marketing Agricultural Products in Agusan Del Sur: A Trifocal Perspective
Authors: Mark Vincent T. Cortez ; Nancy S. Doloriel
Pages: 323-328
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.323.328
Abstract
The research was undertaken on the operational issues in marketing agricultural products from the perspective of three different community sectors in three randomly chosen municipalities in Agusan del Sur—Bunawan, La Paz, and Trento. The eight (8) operational issues identified in the marketing system were evaluated among the agricultural producers, residents, and government officials according to their severity in the community using a Likert Scale. The findings demonstrated that the different sectors of the community viewed the majority of their perceived levels of operational issues with marketing agricultural products as to the economics of agriculture, agriculture product marketing opportunities, land and agriculture, agricultural production practices in the area, the agricultural community in the area, and agriculture and community relations as typically experienced issues in the province’s marketing system. However, the satisfaction with agricultural support as a career and infrastructure revealed the issues evaluated as complicated and complex to handle, respectively. A unisonant evaluative result is implied by the premise that the trifocal perspective by the sectors in the community of the majority challenges in marketing agricultural products revealed no significant variation. Thus, the Department of Agriculture (DA), local government unit (LGU), and other government organizations may consider these results in prioritizing the complicated and complex issues being identified in this study to improve the marketing system in the province of Agusan del Sur.
How to Cite: Mark Vincent T. Cortez, Nancy S. Doloriel, 2023. "Operational Issues of Marketing Agricultural Products in Agusan Del Sur: A Trifocal Perspective." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 323-328.
Ultraviolet-c Radiation Induced Changes on Bioactive Compounds Content, Antioxidant Capacity and Microbial Quality of Minimally Processed Molokhia (Corchorus Olitorius L.) Leaves
Authors: Yousif A. Elhassaneen ; Areeg A. Nour El-Deen ; Amal Z. Nasef
Pages: 309-322
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.309.322
Abstract
Minimally processed or fresh-cut leafy vegetables are very popular for consumption due to their convenience and ready-to-use properties, but they provide an ideal medium for microbial development and degradation of functional properties. Thus, this industry commonly uses chemical agents for disinfection. However, certain problems with the disinfectant agents’ usage have been raised and led to the investigation of alternative sanitization treatments. In this respect, ultraviolet (UV-C) radiation could be of interest because no residues are released and the cost is relatively low. The present study was carried out to investigate the influence of UV-C treatment on bioactive compounds content, antioxidant capacity and microbial quality of minimally processed molokhia (Corchorus olitorius L.) leaves. Data indicated that UV-C irradiation dose (11.35 kJ m−2) of molokhia leaves led to an initial increasing in bioactive compounds including total polyphenols (41.20%), carotenoids (37.41%), flavonoids (26.43%), chlorophyll (11.93%) and lutein (51.73%) in accompanying with slightly decreasing in antioxidant capacity (-11.78%) on processing day. Also, reduction in mesophilic (-11.50), psychrophilic (-18.90) and enterobacteria (-17.10%) counts was also recorded. The initial bioactive compounds and total antioxidant capacity content decreased as well as the bacterium count gradually increased during the storage period in UV-C treated samples for 9 days at 8 0C, especially after 6 days. In conclusion, data of the present study should be taken in our consideration when the UV-C radiation used as alternative to chemical agents for sanitizing minimally processed molokhia leaves and preserving their quality.
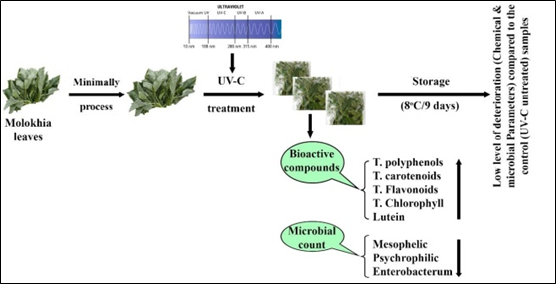
How to Cite: Yousif A. Elhassaneen, Areeg A. Nour El-Deen, Amal Z. Nasef, 2023. "Ultraviolet-c Radiation Induced Changes on Bioactive Compounds Content, Antioxidant Capacity and Microbial Quality of Minimally Processed Molokhia (Corchorus Olitorius L.) Leaves." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 309-322.
Practice of Diabetic Self Care Among Diabetic Farmers in University of Calabar Teaching Hospital Calabar, Nigeria
Authors: Effiong, John B. ; Imaobong O. Enenyi
Pages: 302-308
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.302.308
Abstract
The study analysed the practice of diabetic self care among diabetic farmers in University of Calabar Teaching Hospital Calabar, Nigeria. One hundred and twenty (120) respondents were selected through a multi-stage sampling procedure from diabetic rural farmers attending diabetic clinic in the University of Calabar Teaching Hospital. Data collected were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics such as frequency, percentage, mean, standard deviation and chi-square test respectively. The study revealed that a good proportion (52.5%) of the respondents were males while 47.5% were females. The study revealed through a check list that majority (75.00%) had regular blood glucose check, 70.00 percent had contact with health care providers whenever infections occurred, while 60.83 percent had their meal plan regularly. Constraints affecting diabetic self care practice include lack of technical knowhow on the practice of self care, negative attitude towards diabetes and poor communication between agricultural extension workers, health extension workers and the rural farmers in the study area. The chi square test indicated that, there was no significant relationship between level of education and practice of self-care among diabetic rural farmers in the study area at 5% level of significance with an X2 value of 5.99. The study calls for greater synergy between rural farmers, agricultural extension agents, health workers and diabetic clinics in the study area. This will bring hope and courage to diabetic rural farmers in the study area.
How to Cite: Effiong, J. B., Imaobong O. Enenyi, 2023. "Practice of Diabetic Self Care Among Diabetic Farmers in University of Calabar Teaching Hospital Calabar, Nigeria." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 302-308.
Development and Quality Evaluation of Extruded Breakfast Cereal from Blends of Ofada Rice and Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) with Date Palm Fruit
Authors: Musa Omotayo Jimoh ; Taiwo Olufemi Olurin ; Oyesiku Seun Odunayo
Pages: 293-301
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.293.301
Abstract
Development of food product is a global initiative focused on crops utilization for economic empowerment and service provider. Extruded breakfast cereal developed from unconventional grain, ofada rice blended with cowpea and date palm fruit as natural sweetener was designed and evaluated. Composite flour formulation was in ratio 55:45, 60:40, 65:35, 70:30 while date palm fruit was kept constant. Proximate, functional, pasting, shelf-life and sensory analyses were carried out. Protein and ash content in experimented samples, B1KK, B2KL, B3KM and B4KN increased significantly with increased proportion of cowpea. At 5% level of significance, there was significant difference in water absorption index in all experimented sample while bulk density and swelling power showed no significant difference in most samples. Final viscosity of the samples increased as the proportion of ofada rice decreased while setback viscosity increased as the proportion of cowpea increased. Moisture content, free fatty acid and peroxide value of the samples increased slightly as approaches six weeks storage, however, the result was within internationally acceptable quality limits. Sensory attributes of the designed products are significantly related to the control sample, apparently, consumer perception of the breakfast cereal based products indicated that B2KL was most preferred and thus recommended for commercialization.
How to Cite: Musa Omotayo Jimoh, Taiwo Olufemi Olurin, Oyesiku Seun Odunayo, 2023. "Development and Quality Evaluation of Extruded Breakfast Cereal from Blends of Ofada Rice and Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) with Date Palm Fruit." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 293-301.
Integration of Climate Smart Agro-Technologies and Efficient Post- Harvest Operations in Changing Weather Conditions in Nigeria
Authors: Osuji E. E. ; Anosike F. C. ; Obasi I. O., et. al.
Pages: 281-292
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.281.292
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to examine the integration of climate-smart agro-technologies and efficient post-harvest operations in changing weather conditions in Nigeria. Agriculture, which is the mainstay of most rural families in Nigeria, has faced several problems in recent times as a result of variety of factors such as post-harvest losses, climate change fluctuations, and high poverty level resulting in poor agricultural outputs and low income. Empirical studies have indicated that food production and income growth of farming households would be worse-off, if climate change is not properly mitigated. The combination of climate-smart agro-technologies and effective post-harvest management operations in this era of unfavorable climatic condition and post-harvest losses has become imperative. Climate smart agriculture consists of a three-win approach; for long-term food supply and security. It also comprises of three important goals such as mitigation, adaptation, and increased production. Agro-climate smart technologies includes solar energy techniques for drying agricultural product, green house technology for cultivation, climate resilient storage structures for storing harvested grains, and climate smart waste usage for agricultural waste management. Efficient post-harvest management operations such as proper harvesting, sun-drying, threshing, processing, packaging, and transportations were also explored. This study advocated the adoption of climate smart agro- technologies and efficient post-harvest management operations as an alternative measures for increased food production and farm income in the face of changing weather and climatic conditions.
How to Cite: Osuji E. E., Anosike F. C., Obasi I. O., Nwachukwu E. U., Obi J. N., Orji J. E., Inyang P., Chinaka I. C., Osang E. A., Iroegbu C. S., Nzeakor F. C., Onu S. E., 2023. "Integration of Climate Smart Agro-Technologies and Efficient Post- Harvest Operations in Changing Weather Conditions in Nigeria." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 281-292.
Agroecological Management of Sphenarium Purpurascens with Vegetable Extracts and Entomopathogenic Fungi in Amaranth, Puebla-Mexico
Authors: Emmanuel Rodríguez-Palma ; Agustín Aragón-García ; Betzabeth Cecilia Pérez-Torres, et. al.
Pages: 273-280
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/jac.93.273.280
Abstract
Among the most important pests of amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus L.) is Sphenarium purpurascens Charpentier, 1845 (Orthoptera: Pyrgomorphidae) which causes damage to the plant, decreased performance and economic losses, with chemical products being the main control method. The objective of this work was to evaluate the effect of aqueous extracts of Ricinus communis and Capsicum frutensis combined with two entomopathogenic fungi; one commercial and one native to Puebla-Mexico, alternated with the application of soap, in laboratory and field conditions. Bioassays were carried out to evaluate the compatibility of aqueous extracts with the entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana at concentrations of 25, 50 and 75 % in conidia, in addition, six treatments with five repetitions were tested in a randomized block experimental design in the field. Los bioensayos de laboratorio presentaron diferencias significativas en el desarrollo micelial y tasa de crecimiento, donde se observó un estímulo positivo en el crecimiento de M. anisopliae por parte de los extractos vegetales. In the field, the H+Ch+M treatment registered the least damage (12.9%), least infestation (1.1%) and best seed production (1,353.7 kg/Ha). The effect of aqueous extracts combined with M. anisopliae, alternated with soap applications, proved to be an effective strategy in the integrated management of Sphenarium purpurascens, in amaranth cultivation in Puebla, Mexico.
How to Cite: Emmanuel Rodríguez-Palma, Betzabeth Cecilia Pérez-Torres, Jesús Francisco López-Olguín, Omar Romero-Arenas, Miguel Aragón Sánchez, 2023. "Agroecological Management of Sphenarium Purpurascens with Vegetable Extracts and Entomopathogenic Fungi in Amaranth, Puebla-Mexico." Journal of Agriculture and Crops, vol. 9, pp. 273-280.



