Academic Journal of Applied Mathematical Sciences
Online ISSN: 2415-2188
Print ISSN: 2415-5225
Print ISSN: 2415-5225
Quarterly Published (4 Issues Per Year)

Archives
Volume 6 Number 8 October 2020
Increasing the Accuracy of the Difference Scheme Using the Richardson Extrapolation Based on the Movable Node Method
Authors: Umurdin Dalabaev
Pages: 204-212
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/ajams.68.204.212
Abstract
A one-dimensional convective-diffusion problem is considered. To improve the quality of difference schemes, the method of moving nodes is used in combination with Richardson interpolation. Approximate analytical solutions and improved schemes are obtained. Numerical experiments carried out.
Handling Outliers and Missing Data in Regression Models Using R: Simulation Examples
Authors: Mohamed Reda Abonazel
Pages: 187-203
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/ajams.68.187.203
Abstract
This paper has reviewed two important problems in regression analysis (outliers and missing data), as well as some handling methods for these problems. Moreover, two applications have been introduced to understand and study these methods by R-codes. Practical evidence was provided to researchers to deal with those problems in regression modeling with R. Finally, we created a Monte Carlo simulation study to compare different handling methods of missing data in the regression model. Simulation results indicate that, under our simulation factors, the k-nearest neighbors method is the best method to estimate the missing values in regression models.
A Note on Different Types of Probabilities of Misclassification
Authors: Awogbemi Clement Adeyeye
Pages: 181-186
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/ajams.68.181.186
Abstract
Whenever a discriminant function is constructed, the attention of a researcher is often focused on classification. The underlined interest is how well does a discriminant function perform in classifying future observations correctly. In order to assess the performance of any classification rule, probabilities of misclassification of a discriminant function serves as a basis for the procedure. Different forms of probabilities of misclassification and their associated properties were considered in this study. The misclassification probabilities were defined in terms of probability density functions (pdf) and classification regions. Apparent probability of misclassification is expressed as the proportion of observations in the initial sample which are misclassified by the sample discriminant function. Different methods of estimating probabilities of misclassification were related to each other using their individual shortcomings. The status of degrees of uncertainties associated with probabilities of misclassification and their implications were also specified.
Forecasting of COVID-19 Cases in Kurdistan Region Using Some Statistical Models
Authors: Shekhmous Hassan Hussen
Pages: 172-180
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/ajams.68.172.180
Abstract
Nowadays the new universal disease of the coronavirus that is called the epidemic COVID-19 is spread as geometric progression among the people around the world, so, such pathogen considered the most dangerous threat facing humanity. This study aimed to derive the best forecasting models for the close future cases of infected, recovered, and deaths in the four provinces of Kurdistan Region-Iraq to avoid more loss of human lives by applying more health care in certain province. Two forecasting methods were used including Exponential Smoothing and ARIMA models. The results indicate that both ARIMA and Exponential Smoothing models were close to each other for predicting the infected cases of COVID-19 in Kurdistan Region provinces, and the predicting models show that the pandemic might not be under control unless the people apply the government instructions for health care and keep social distances.
A Peer Search on Integer Solutions to Quadratic Diophantine Equation with Three Unknowns
![]()
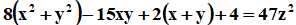
Authors: A. Vijayasankar ; Sharadha Kumar ; M. A. Gopalan
Pages: 166-171
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/ajams.68.166.171
Abstract
The non- homogeneous ternary quadratic diophantine equation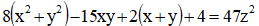 is analyzed for its patterns of non-zero distinct integral solutions. Various interesting relations between the solutions and special numbers namely polygonal, Pronic and Gnomonic numbers are exhibited.
is analyzed for its patterns of non-zero distinct integral solutions. Various interesting relations between the solutions and special numbers namely polygonal, Pronic and Gnomonic numbers are exhibited.
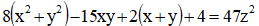 is analyzed for its patterns of non-zero distinct integral solutions. Various interesting relations between the solutions and special numbers namely polygonal, Pronic and Gnomonic numbers are exhibited.
is analyzed for its patterns of non-zero distinct integral solutions. Various interesting relations between the solutions and special numbers namely polygonal, Pronic and Gnomonic numbers are exhibited.
Annotations on the Relationship Among Discriminant Functions
Authors: Awogbemi Clement Adeyeye
Pages: 161-165
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/ajams.68.161.165
Abstract
Different forms of discriminant functions and the essence of their appearances were considered in this study. Various forms of classification problems were also considered, and in each of the cases mentioned, classification from simple functions of the observational vector rather than complicated regions in the higher-dimensional space of the original vector were made. Violation of condition of equal variance covariance matrix for Linear Discriminant Function (LDF) results to Quadratic Discriminant Function (QDF). The relationships among the classification statistics examined were established: The Anderson’s (W) and Rao’s (R) statistics are equivalent when the two sample sizes are equal, and when a constant is equal to 1, W, R and John-Kudo’s (Z) classification statistics are asymptotically comparable. A linear relationship is also established between W and Z classification statistics.
Response Triggered Architecture for E-Payment Examined for General Purpose Transaction
Authors: Akomolafe Dipo Theophilus ; Adeola Oladele Stephen
Pages: 153-160
DOI: doi.org/10.32861/ajams.68.153.160
Abstract
The explosive growth in internet coupled with advancement in Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has made business transactions much easier than it used to be in the past. For example, e-commerce has particularly benefited from the introduction of GSM system. One of the major challenges, however, is how to isolate fraudulent transactions from genuine businesses. This becomes more imperative as the advancement in ICT has brought with it fraud and related scams. In this work, we examined different types of e-commerce as well as the challenges being encountered in the course of daily transactions. We took advantage of the current trends in mobile communication networks, particularly GSM and proposed a system based on Response Triggered Architecture for electronic transaction. Our proposed system is platform independent which means only little modification is needed when switching from one platform to another. We used Visual.basic.net and knowledge in fraud for our system prototype and presented the results in the body of this work.



